Down’s Syndrome Screening & Diagnosis
Diagnostic tests such as (amniocentesis and CVS) are done to test for Down’s syndrome. Diagnostic tests are definitive tests and give a yes/no answer. Thus the test results, if normal, will reassure the pregnant mother to continue the pregnancy and become tension free for the rest of the pregnancy. While in screening tests, a probability is generated and if the probability is high, a diagnostic test like amniocentesis or CVS is indicated. Dr. Pawar has been doing amniocentesis and CVS since 2005 (an experience of 15 years as Fetal Medicine Specialist)
Screening tests during pregnancy
Screening for Down syndrome is offered as a routine part of prenatal care. Although screening tests can only identify your risk of carrying a baby with Down syndrome, they can help you make decisions about more-specific diagnostic tests.
Screening tests include the first trimester combined test and the integrated screening test.
The first trimester combined test
The first trimester combined test, which is done in two steps, includes:
- Blood test. This blood test measures the levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A) and the pregnancy hormone known as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). Abnormal levels of PAPP-A and HCG may indicate a problem with the baby.
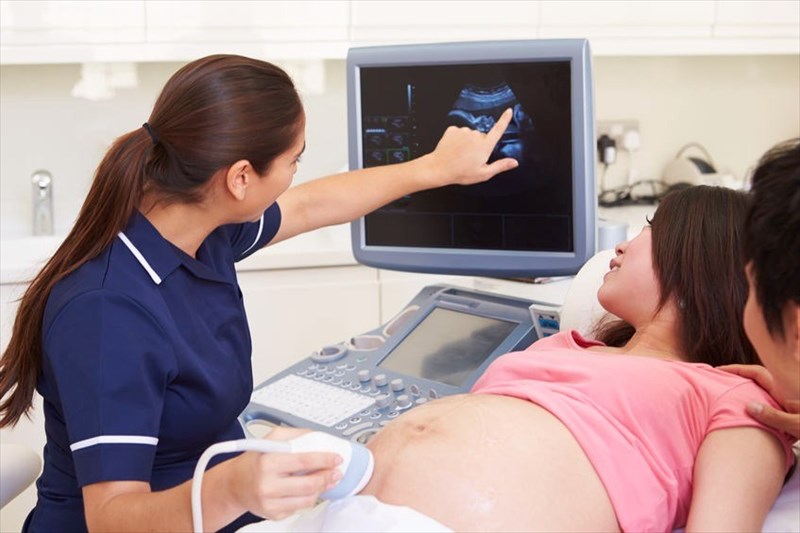
- Nuchal translucency test. During this test, an ultrasound is used to measure a specific area on the back of your baby’s neck. This is known as a nuchal translucency screening test. When abnormalities are present, more fluid than usual tends to collect in this neck tissue.
Using your age and the results of the blood test and the ultrasound, your doctor or genetic counselor can estimate your risk of having a baby with Down syndrome.
Integrated screening test
The integrated screening test is done in two parts during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. The results are combined to estimate the risk that your baby has Down syndrome.
- First trimester. Part one includes a blood test to measure PAPP-A and an ultrasound to measure nuchal translucency.
- Second trimester. The quad screen measures your blood level of four pregnancy-associated substances: alpha fetoprotein, estriol, HCG and inhibin A.
Diagnostic tests during pregnancy
If your screening test results are positive or worrisome, or you’re at high risk of having a baby with Down syndrome, you might consider more testing to confirm the diagnosis. Your health care provider can help you weigh the pros and cons of these tests.
Diagnostic tests that can identify Down syndrome include:
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). In CVS, cells are taken from the placenta and used to analyze the fetal chromosomes. This test is typically performed in the first trimester, between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. The risk of pregnancy loss (miscarriage) from a CVS is very low.
- Amniocentesis. A sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is withdrawn through a needle inserted into the mother’s uterus. This sample is then used to analyze the chromosomes of the fetus. Doctors usually perform this test in the second trimester, after 15 weeks of pregnancy. This test also carries a very low risk of miscarriage.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is an option for couples undergoing in vitro fertilization who are at increased risk of passing along certain genetic conditions. The embryo is tested for genetic abnormalities before it’s implanted in the womb.
Dr. Rajeshwari Pawar
Services including pregnancy care, fetal care, pregnancy sonography and laboratory investigations